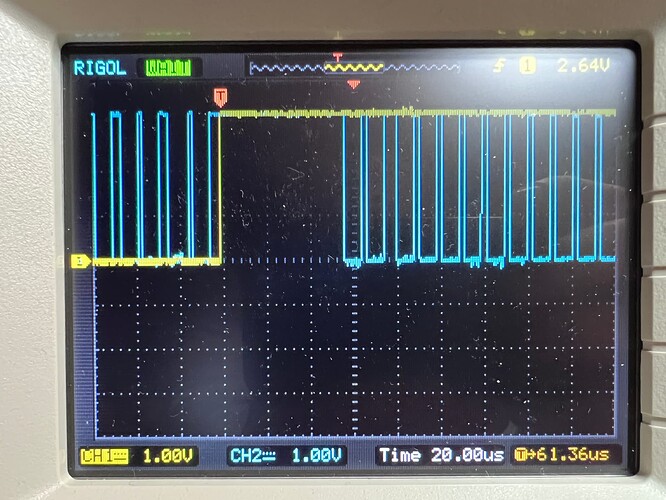
I was able to get this working for AVR128DB28 with the changes mentioned above. I’m also very happy that I was able to get it working with ATtiny84!
I created a fork and put in a pull request with the proposed additions. https://github.com/openenergymonitor/RFM69_LPL/pull/2
Here is the updated library code and a test sketch that works for both chips using DxCore and ATTinyCore, respectively.
Library code.
// **********************************************************************************
// Driver definition for HopeRF RFM69W/RFM69HW/RFM69CW/RFM69HCW, Semtech SX1231/1231H
// **********************************************************************************
// Copyright LowPowerLab LLC 2018, https://www.LowPowerLab.com/contact
// **********************************************************************************
// License
// **********************************************************************************
// This program is free software; you can redistribute it
// and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General
// Public License as published by the Free Software
// Foundation; either version 3 of the License, or
// (at your option) any later version.
//
// This program is distributed in the hope that it will
// be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the
// implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A
// PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public
// License for more details.
//
// Licence can be viewed at
// http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.txt
//
// Please maintain this license information along with authorship
// and copyright notices in any redistribution of this code
// **********************************************************************************
#include "RFM69_LPL.h"
#include "RFM69_LPL_registers.h"
uint8_t RFM69::DATA[RF69_MAX_DATA_LEN+1];
uint8_t RFM69::_mode; // current transceiver state
uint8_t RFM69::DATALEN;
uint16_t RFM69::SENDERID;
uint16_t RFM69::TARGETID; // should match _address
uint8_t RFM69::PAYLOADLEN;
uint8_t RFM69::ACK_REQUESTED;
uint8_t RFM69::ACK_RECEIVED; // should be polled immediately after sending a packet with ACK request
int16_t RFM69::RSSI; // most accurate RSSI during reception (closest to the reception)
bool RFM69::initialize (uint8_t freqBand, uint16_t ID, uint8_t networkID) {
_address = ID;
_retrycount = 0;
// 10 MHz, i.e. 30 MHz / 3 (or 4 MHz if clock is still at 12 MHz)
spi_init();
uint32_t start = millis();
uint8_t timeout = 50;
do writeReg(REG_SYNCVALUE1, 0xAA); while (readReg(REG_SYNCVALUE1) != 0xaa && millis()-start < timeout);
if (millis()-start >= timeout) return false;
start = millis();
do writeReg(REG_SYNCVALUE1, 0x55); while (readReg(REG_SYNCVALUE1) != 0x55 && millis()-start < timeout);
if (millis()-start >= timeout) return false;
const uint8_t configRegs [] = {
0x01, 0x04,
0x02, 0x00,
0x03, 0x02, // MSB 55555 bits/s
0x04, 0x40, // LSB 55555 bits/s
0x05, 0x03, // MSB FDEV 50000
0x06, 0x33, // LSB FDEV 50000
0x07, (uint8_t)(freqBand == RF69_868MHZ?0xD9:0x6C), // MSB 433 Mhz
0x08, (uint8_t)(freqBand == RF69_868MHZ?0x00:0x40), // MID 433 Mhz
0x09, (uint8_t)(freqBand == RF69_868MHZ?0x00:0x00), // LSB 433 Mhz
0x19, 0x42, // REG_RXBW (BitRate < 2 * RxBw)
0x25, 0x40, // DIO0 is the only IRQ we're using
0x26, 0x07, // DIO5 ClkOut disable for power saving
0x28, 0x10, // REG_IRQFLAGS2, RF_IRQFLAGS2_FIFOOVERRUN writing to this bit ensures that the FIFO & status flags are reset
0x29, 0xDC, // REG_RSSITHRESH must be set to dBm = (-Sensitivity / 2), default is 0xE4 = 228 so -114dBm
0x2E, 0x88, // RF_SYNC_ON | RF_SYNC_FIFOFILL_AUTO | RF_SYNC_SIZE_2 | RF_SYNC_TOL_0
0x2F, 0x2D, // attempt to make this compatible with sync1 byte of RFM12B lib
0x30, networkID, // networkID
0x37, 0x90, // RF_PACKET1_FORMAT_VARIABLE | RF_PACKET1_DCFREE_OFF | RF_PACKET1_CRC_ON | RF_PACKET1_CRCAUTOCLEAR_ON | RF_PACKET1_ADRSFILTERING_OFF
0x38, 66, // in variable length mode: the max frame size, not used in TX
0x3C, 0x8F, // TX on FIFO not empty
0x3D, 0x10, // RXRESTARTDELAY must match transmitter PA ramp-down time (bitrate dependent)
0x6F, 0x30, // run DAGC continuously in RX mode for Fading Margin Improvement, recommended default for AfcLowBetaOn=0
0
};
configure(configRegs);
// Encryption is persistent between resets and can trip you up during debugging.
// Disable it during initialization so we always start from a known state.
encrypt(0);
uint8_t powerLevel = 25; // could be up to 31... -18 + dBm with PA0 = 7dBm
if (powerLevel>31) powerLevel = 31;
writeReg(0x11,RF_PALEVEL_PA0_ON | powerLevel);
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY);
start = millis();
while (((readReg(REG_IRQFLAGS1) & RF_IRQFLAGS1_MODEREADY) == 0x00) && millis()-start < timeout); // wait for ModeReady
if (millis()-start >= timeout)
return false;
return true;
}
void RFM69::setPins (uint8_t _SSpin, uint8_t _MOSIpin, uint8_t _MISOpin, uint8_t _SCKpin) {
SSpin = _SSpin;
MOSIpin = _MOSIpin;
MISOpin = _MISOpin;
SCKpin = _SCKpin;
#ifdef __AVR_DB__
if (MOSIpin==PIN_PA4 && MISOpin==PIN_PA5 && SCKpin==PIN_PA6) {
SPI_PORT = 0;
} else if (MOSIpin==PIN_PC0 && MISOpin==PIN_PC1 && SCKpin==PIN_PC2) {
SPI_PORT = 1;
}
#endif
}
void RFM69::setMode (uint8_t newMode) {
if (newMode == _mode)
return;
writeReg(REG_OPMODE, (readReg(REG_OPMODE) & 0xE3) | newMode);
// we are using packet mode, so this check is not really needed
// but waiting for mode ready is necessary when going from sleep because the FIFO may not be immediately available from previous mode
while (_mode == RF69_MODE_SLEEP && (readReg(REG_IRQFLAGS1) & RF_IRQFLAGS1_MODEREADY) == 0x00); // wait for ModeReady
_mode = newMode;
}
//put transceiver in sleep mode to save battery - to wake or resume receiving just call receiveDone()
void RFM69::sleep() {
setMode(RF69_MODE_SLEEP);
}
//set this node's address
void RFM69::setAddress(uint16_t addr)
{
_address = addr;
writeReg(REG_NODEADRS, _address); //unused in packet mode
}
bool RFM69::canSend()
{
if (_mode == RF69_MODE_RX && PAYLOADLEN == 0 && readRSSI() < CSMA_LIMIT) // if signal stronger than -100dBm is detected assume channel activity
{
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY);
return true;
}
return false;
}
void RFM69::send(uint16_t toAddress, const void* buffer, uint8_t bufferSize, bool requestACK)
{
writeReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2, (readReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2) & 0xFB) | RF_PACKET2_RXRESTART); // avoid RX deadlocks
uint32_t now = millis();
while (!canSend() && millis() - now < RF69_CSMA_LIMIT_MS){
receiveDone();
}
sendFrame(toAddress, buffer, bufferSize, requestACK, false);
}
// to increase the chance of getting a packet across, call this function instead of send
// and it handles all the ACK requesting/retrying for you :)
// The only twist is that you have to manually listen to ACK requests on the other side and send back the ACKs
// The reason for the semi-automaton is that the lib is interrupt driven and
// requires user action to read the received data and decide what to do with it
// replies usually take only 5..8ms at 50kbps@915MHz
bool RFM69::sendWithRetry(uint16_t toAddress, const void* buffer, uint8_t bufferSize, uint8_t retries, uint8_t retryWaitTime) {
uint32_t sentTime;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i <= retries; i++)
{
_retrycount = i;
send(toAddress, buffer, bufferSize, true);
sentTime = millis();
while (millis() - sentTime < retryWaitTime)
{
if (ACKReceived(toAddress)) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
uint8_t RFM69::retry_count() {
return _retrycount;
}
// should be polled immediately after sending a packet with ACK request
bool RFM69::ACKReceived(uint16_t fromNodeID) {
if (receiveDone())
return (SENDERID == fromNodeID || fromNodeID == RF69_BROADCAST_ADDR) && ACK_RECEIVED;
return false;
}
// check whether an ACK was requested in the last received packet (non-broadcasted packet)
bool RFM69::ACKRequested() {
return ACK_REQUESTED && (TARGETID == _address);
}
// should be called immediately after reception in case sender wants ACK
void RFM69::sendACK(const void* buffer, uint8_t bufferSize) {
ACK_REQUESTED = 0; // TWS added to make sure we don't end up in a timing race and infinite loop sending Acks
uint16_t sender = SENDERID;
int16_t _RSSI = RSSI; // save payload received RSSI value
writeReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2, (readReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2) & 0xFB) | RF_PACKET2_RXRESTART); // avoid RX deadlocks
uint32_t now = millis();
while (!canSend() && millis() - now < RF69_CSMA_LIMIT_MS){
receiveDone();
}
SENDERID = sender; // TWS: Restore SenderID after it gets wiped out by receiveDone()
sendFrame(sender, buffer, bufferSize, false, true);
RSSI = _RSSI; // restore payload RSSI
}
// internal function
void RFM69::sendFrame(uint16_t toAddress, const void* buffer, uint8_t bufferSize, bool requestACK, bool sendACK)
{
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY); // turn off receiver to prevent reception while filling fifo
while ((readReg(REG_IRQFLAGS1) & RF_IRQFLAGS1_MODEREADY) == 0x00); // wait for ModeReady
if (bufferSize > RF69_MAX_DATA_LEN) bufferSize = RF69_MAX_DATA_LEN;
// control byte
uint8_t CTLbyte = 0x00;
if (sendACK)
CTLbyte = RFM69_CTL_SENDACK;
else if (requestACK)
CTLbyte = RFM69_CTL_REQACK;
if (toAddress > 0xFF) CTLbyte |= (toAddress & 0x300) >> 6; //assign last 2 bits of address if > 255
if (_address > 0xFF) CTLbyte |= (_address & 0x300) >> 8; //assign last 2 bits of address if > 255
// write to FIFO
select();
spi_transfer(REG_FIFO | 0x80);
spi_transfer(bufferSize + 3);
spi_transfer((uint8_t)toAddress);
spi_transfer((uint8_t)_address);
spi_transfer(CTLbyte);
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < bufferSize; i++)
spi_transfer(((uint8_t*) buffer)[i]);
unselect();
// no need to wait for transmit mode to be ready since its handled by the radio
setMode(RF69_MODE_TX);
while ((readReg(REG_IRQFLAGS2) & RF_IRQFLAGS2_PACKETSENT) == 0x00); // wait for packet sent
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY);
}
// internal function - interrupt gets called when a packet is received
void RFM69::interruptHandler() {
if (_mode == RF69_MODE_RX && (readReg(REG_IRQFLAGS2) & RF_IRQFLAGS2_PAYLOADREADY))
{
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY);
select();
spi_transfer(REG_FIFO & 0x7F);
PAYLOADLEN = spi_transfer(0);
PAYLOADLEN = PAYLOADLEN > 66 ? 66 : PAYLOADLEN; // precaution
TARGETID = spi_transfer(0);
SENDERID = spi_transfer(0);
uint8_t CTLbyte = spi_transfer(0);
TARGETID |= (uint16_t(CTLbyte) & 0x0C) << 6; //10 bit address (most significant 2 bits stored in bits(2,3) of CTL byte
SENDERID |= (uint16_t(CTLbyte) & 0x03) << 8; //10 bit address (most sifnigicant 2 bits stored in bits(0,1) of CTL byte
if(!(TARGETID == _address || TARGETID == RF69_BROADCAST_ADDR) // match this node's address, or broadcast address or anything in spy mode
|| PAYLOADLEN < 3) // address situation could receive packets that are malformed and don't fit this libraries extra fields
{
PAYLOADLEN = 0;
unselect();
receiveBegin();
return;
}
DATALEN = PAYLOADLEN - 3;
ACK_RECEIVED = CTLbyte & RFM69_CTL_SENDACK; // extract ACK-received flag
ACK_REQUESTED = CTLbyte & RFM69_CTL_REQACK; // extract ACK-requested flag
// uint8_t _pl = _powerLevel; //interruptHook() can change _powerLevel so remember it
// interruptHook(CTLbyte); // TWS: hook to derived class interrupt function
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < DATALEN; i++) DATA[i] = spi_transfer(0);
DATA[DATALEN] = 0; // add null at end of string // add null at end of string
unselect();
setMode(RF69_MODE_RX);
// if (_pl != _powerLevel) setPowerLevel(_powerLevel); //set new _powerLevel if changed
RSSI = readRSSI();
}
}
void RFM69::receiveBegin() {
DATALEN = 0;
SENDERID = 0;
TARGETID = 0;
PAYLOADLEN = 0;
ACK_REQUESTED = 0;
ACK_RECEIVED = 0;
RSSI = 0;
if (readReg(REG_IRQFLAGS2) & RF_IRQFLAGS2_PAYLOADREADY)
writeReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2, (readReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2) & 0xFB) | RF_PACKET2_RXRESTART); // avoid RX deadlocks
// writeReg(REG_DIOMAPPING1, RF_DIOMAPPING1_DIO0_01); // set DIO0 to "PAYLOADREADY" in receive mode
setMode(RF69_MODE_RX);
}
// checks if a packet was received and/or puts transceiver in receive (ie RX or listen) mode
bool RFM69::receiveDone() {
interruptHandler();
if (_mode == RF69_MODE_RX && PAYLOADLEN > 0)
{
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY); // enables interrupts
return true;
}
else if (_mode == RF69_MODE_RX) // already in RX no payload yet
{
return false;
}
receiveBegin();
return false;
}
// To enable encryption: radio.encrypt("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP");
// To disable encryption: radio.encrypt(null) or radio.encrypt(0)
// KEY HAS TO BE 16 bytes !!!
void RFM69::encrypt(const char* key) {
setMode(RF69_MODE_STANDBY);
uint8_t validKey = key != 0 && strlen(key)!=0;
if (validKey)
{
select();
spi_transfer(REG_AESKEY1 | 0x80);
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 16; i++)
spi_transfer(key[i]);
unselect();
}
writeReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2, (readReg(REG_PACKETCONFIG2) & 0xFE) | (validKey ? 1 : 0));
}
// get the received signal strength indicator (RSSI)
int16_t RFM69::readRSSI(bool forceTrigger) {
int16_t rssi = 0;
if (forceTrigger)
{
// RSSI trigger not needed if DAGC is in continuous mode
writeReg(REG_RSSICONFIG, RF_RSSI_START);
while ((readReg(REG_RSSICONFIG) & RF_RSSI_DONE) == 0x00); // wait for RSSI_Ready
}
rssi = -readReg(REG_RSSIVALUE);
rssi >>= 1;
return rssi;
}
uint8_t RFM69::readReg(uint8_t addr)
{
select();
spi_transfer(addr & 0x7F);
uint8_t regval = spi_transfer(0);
unselect();
return regval;
}
void RFM69::writeReg(uint8_t addr, uint8_t value)
{
select();
spi_transfer(addr | 0x80);
spi_transfer(value);
unselect();
}
void RFM69::select() {
#ifdef __AVR_ATmega328P__
PORTB &= ~(1 << PORTB2); // faster direct port manipulation, may not be necessary
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_DB__
#ifdef PIN_PB5 //PIN_PB5 is specific to DB48 and not defined on DB28
if (SSpin==PIN_PB5) {
digitalWriteFast(PIN_PB5, 0);
}
#endif
if (SSpin==PIN_PA7) {
digitalWriteFast(PIN_PA7, 0);
}
else if (SSpin==PIN_PC3) {
digitalWriteFast(PIN_PC3, 0);
}
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_ATtinyX4__
if (SSpin==PIN_PB1) {
digitalWrite(PIN_PB1, 0);
}
#endif
}
void RFM69::unselect() {
#ifdef __AVR_ATmega328P__
PORTB |= (1 << PORTB2); // faster direct port manipulation, may not be necessary
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_DB__
#ifdef PIN_PB5 //PIN_PB5 is specific to DB48 and not defined on DB28
if (SSpin==PIN_PB5) {
digitalWriteFast(PIN_PB5, 1);
}
#endif
if (SSpin==PIN_PA7) {
digitalWriteFast(PIN_PA7, 1);
}
else if (SSpin==PIN_PC3) {
digitalWriteFast(PIN_PC3, 1);
}
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_ATtinyX4__
if (SSpin==PIN_PB1) {
digitalWrite(PIN_PB1, 1);
}
#endif
}
void RFM69::spi_init() {
pinMode(SSpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOSIpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MISOpin, INPUT);
pinMode(SCKpin, OUTPUT);
unselect();
#ifdef __AVR_ATmega328P__
SPCR = _BV(SPE) | _BV(MSTR);
SPSR |= _BV(SPI2X);
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_DB__
if (SPI_PORT==0) {
PORTMUX.SPIROUTEA = SPI_MUX | (PORTMUX.SPIROUTEA & (~PORTMUX_SPI0_gm));
SPI0.CTRLB |= (SPI_SSD_bm);
SPI0.CTRLA |= (SPI_ENABLE_bm | SPI_MASTER_bm);
} else {
PORTMUX.SPIROUTEA = SPI_MUX | (PORTMUX.SPIROUTEA & (~PORTMUX_SPI1_gm));
SPI1.CTRLB |= (SPI_SSD_bm);
SPI1.CTRLA |= (SPI_ENABLE_bm | SPI_MASTER_bm);
}
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_ATtinyX4__
USICR = bit(USIWM0);
#endif
}
uint8_t RFM69::spi_transfer (uint8_t data) {
#ifdef __AVR_ATmega328P__
SPDR = data;
while ((SPSR & (1<<SPIF)) == 0)
;
return SPDR;
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_DB__
asm volatile("nop");
if (SPI_PORT==0) {
SPI0.DATA = data;
while ((SPI0.INTFLAGS & SPI_RXCIF_bm) == 0); // wait for complete send
return SPI0.DATA; // read data back
} else {
SPI1.DATA = data;
while ((SPI1.INTFLAGS & SPI_RXCIF_bm) == 0); // wait for complete send
return SPI1.DATA; // read data back
}
return 0;
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_ATtinyX4__
USIDR = data;
byte v1 = bit(USIWM0) | bit(USITC);
byte v2 = bit(USIWM0) | bit(USITC) | bit(USICLK);
#if F_CPU <= 5000000
//unroll if clock is under 2.5 MHz
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
USICR = v1; USICR = v2;
#else
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
USICR = v1;
USICR = v2;
}
#endif
return USIDR;
#endif
}
void RFM69::configure (const uint8_t* p) {
while (true) {
uint8_t cmd = p[0];
if (cmd == 0)
break;
writeReg(cmd, p[1]);
p += 2;
}
}
Test sketch.
/* Brandock 2023
* Test sender for RFM69_LPL Open Energy Monitor fork.
* Works with ATmega328, ATtiny84A, and AVR128DB28. The later two pin mappings shown below.
* The later two chips require an update to the forked library as of 5/20/23. See the forum post
* https://community.openenergymonitor.org/t/help-with-oem-fork-of-rfm69-lpl-avr128db28-and-maybe-someday-attiny84/23530/7
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
* ATMEL ATTINY84/44/24 ATTinyCore Standard (Clockwise) Pin Mapping
*
* +-\/-+
* VCC 1| |14 GND
* (10) PB0 2|x a|13 PA0 ( 0)
* SEL ( 9) PB1 3|x a|12 PA1 ( 1) AIN0/TX
* (11) PB3 4| a|11 PA2 ( 2) AIN1/RX
* ( 8) PB2 5| a|10 PA3 ( 3)
* LED ( 7) PA7 6|a a|9 PA4 ( 4) SCK
* MISO ( 6) PA6 7|a a|8 PA5 ( 5) MOSI
* +----+
*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
* ATMEL AVR128DB28 DxCore Pin Mapping
* Note: The SPI0 and SPI1 MUX is the same on the 48-pin part and 28-pin AVR-DB.
*
* +-\/-+
* LED/SS0 ( 7) PA7 1| |28 PA6 .( 6) SCK0
* MOSI1 ( 8) PC0 2| |13 PA5 ( 5) MISO0
* MISO1 ( 9) PC1 3| |12 PA4 ( 4) MOSI0
* SCK1 (10) PC2 4| |11 PA3 ( 3)
* SEL1 (11) PC3 5| |10 PA2 ( 2)
* VDDDI02 6| |9 PA1 ( 1) RXD0
* (13) PD1 7| |8 PA0 ( 0) TXD0
* : :
*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
* In this sketch: DB28 Pin Mapping
*
* Use the SPI1 MUX for the RFM transceiver. Before initializing the radio set the pins:
* radio.setPins(PIN_PC3,PIN_PC0,PIN_PC1,PIN_PC2);
* //(SEL ,MOSI ,MISO, ,SCK )
*
* We choose the SPI1 MUX for three reasons:
* 1. Uses Port C, which can run at VDDIO2, which is good for 3V3 radios if VDD is 5V.
* 2. Makes PA7 available for LED_BUILTIN, which is not a huge deal, but is nice.
* 3. This is the same MUX used by OpenEnergyMonitor for emonTx v4.
* Note: emonTx4 uses PB5 for SEL. That pin is not available on the 28-pin part, so we use PC3.
* +-\/-+
* LED ( 7) PA7 1| |28 PA6 .( 6)
* MOSI1 ( 8) PC0 2| |13 PA5 ( 5)
* MISO1 ( 9) PC1 3| |12 PA4 ( 4)
* SCK1 (10) PC2 4| |11 PA3 ( 3)
* SEL1 (11) PC3 5| |10 PA2 ( 2)
* VDDDI02 6| |9 PA1 ( 1) RXD0
* (13) PD1 7| |8 PA0 ( 0) TXD0
* : :
*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*For ATtiny84 there are two pin numbering schemes. This is how to check the settings used to compile the sketch. It is not necessary here because we use the agnostic PIN_Pxn method. */
#ifdef PINMAPPING_CCW
#error "For ATTinyCore use clockwise pin mapping option in Arduino > Tools menu options. This sketch uses the clockwise pin map."
#endif
#include <RFM69_LPL.h>
//#include <RFM69_ATC.h> //get it here: https://github.com/amadeuspzs/RFM69
//#include <SPI.h> //included with Arduino IDE install (www.arduino.cc)
//#include <SPIFlash.h>
//#include <WirelessHEX69.h> //get it here: https://github.com/LowPowerLab/WirelessProgramming
//#include "EmonLib.h"
#define debug true
#define NODEID 18
#define NETWORKID 100
#define GATEWAYID 1
#define FREQUENCY RF69_433MHZ //Match this with the version of your Moteino! (others: RF69_433MHZ, RF69_868MHZ)
#if (defined(__AVR_ATtinyX4__))
#define LED PIN_PA7
#elif (defined(__AVR_DB__))
#define LED PIN_PA7
#else
#define LED 9 //Moteinos, for example use D9. D2 is available when using OEM RFM69_LPL (not used as IRQ) if not connected to RFM69
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_ATtinyX4__
#define SERIAL_BAUD 9600
#else
#define SERIAL_BAUD 115200
#endif
#define ACK_TIME 30 // # of ms to wait for an ack
int TRANSMITPERIOD = 5000; //transmit a packet to gateway so often (in ms)
byte sendSize=0;
boolean requestACK = true;
char buffer[50];
//SPIFlash flash(8, 0xEF30); //EF40 for 16mbit windbond chip
int counter = 1;
RFM69 radio;
//EnergyMonitor emon1;
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
pinMode(LED,OUTPUT);
if (debug) Serial.begin(SERIAL_BAUD);
//Set the pins for the SPI radio MUX using
//setPins(uint8_t _SSpin, uint8_t _MOSIpin, uint8_t _MISOpin, uint8_t _SCKpin)
//Defaults in RFM69_LPL.h are (10,11,12,13) for ATMega328
#ifdef __AVR_ATtinyX4__
radio.setPins(PIN_PB1,PIN_PA5,PIN_PA6,PIN_PA4);
#endif
#ifdef __AVR_DB__
#ifdef DEFAULT_28PIN_PINOUT //Use this to detect the 28-pin part
//radio.setPins(PIN_PA7,PIN_PA4,PIN_PA5,PIN_PA6); //SP0 MUX on AVR128DB28
radio.setPins(PIN_PC3,PIN_PC0,PIN_PC1,PIN_PC2); //SPI1 MUX on AVR128DB28
#else
radio.setPins(PIN_PB5,PIN_PC0,PIN_PC1,PIN_PC2); //AVR128DB48
#endif
#endif
if (debug) Serial.println("Initializing Radio...");
Blink(LED,300); delay(100);
Blink(LED,300); delay(100);
Blink(LED,300); delay(500);
radio.initialize(FREQUENCY,NODEID,NETWORKID);
if (debug) Serial.println("Done.");
Blink(LED,300); delay(100);
Blink(LED,300); delay(100);
Blink(LED,300); delay(500);
//emon1.current(0, 13.82);
}
void loop() {
//check for any received packets
if (radio.receiveDone())
{
if (debug) Serial.print('[');Serial.print(radio.SENDERID, DEC);Serial.print("] ");
for (byte i = 0; i < radio.DATALEN; i++)
if (debug) Serial.print((char)radio.DATA[i]);
if (debug) Serial.print(" [RX_RSSI:");Serial.print(radio.readRSSI());Serial.print("]");
// wireless programming token check
// CheckForWirelessHEX(radio, flash, true);
if (radio.ACKRequested())
{
radio.sendACK();
if (debug) Serial.print(" - ACK sent");
delay(10);
}
Blink(LED,300);
Serial.println();
}
// double Irms = emon1.calcIrms(1480); // Calculate Irms only
if (debug) Serial.print("Sending: ");
if (debug) Serial.print(counter);
sprintf(buffer,"%d %d",NODEID,counter);
//radio.sendWithRetry(GATEWAYID, buffer, strlen(buffer), 1); //retry one time
//radio.send(GATEWAYID, buffer, strlen(buffer), requestACK); //send without retry, requestACK depends on definition of requestACK
if (radio.sendWithRetry(GATEWAYID, buffer, strlen(buffer), 1, 120)) { //retry once, 60 ms wait for ACK. Blink once if successfull, twice if not.
if (debug) Serial.println(" ok!");
Blink(LED,600);
} else {
if (debug) Serial.println(" nothing...");
Blink(LED,200); delay(200);
Blink(LED,200);
}
counter++;
delay(5000); //seconds * 1000
}
void Blink(byte PIN, int DELAY_MS)
{
pinMode(PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(PIN,HIGH);
delay(DELAY_MS);
digitalWrite(PIN,LOW);
}